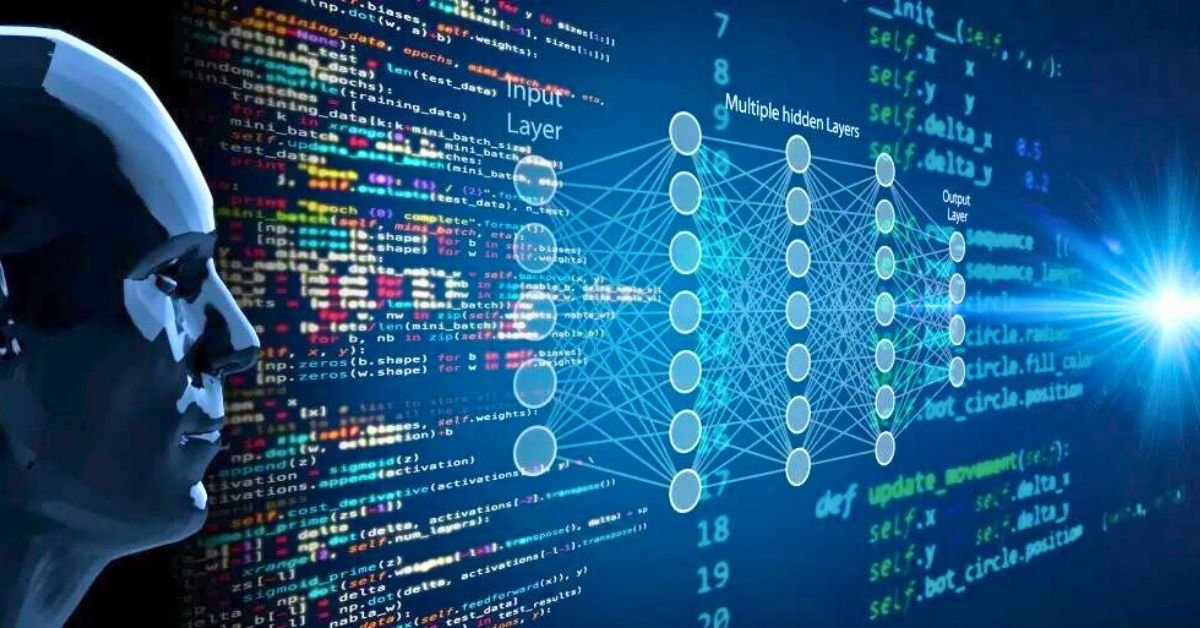
Computer technology has revolutionised our world, transforming how we communicate, work, and live. From the early days of computing to today’s advanced systems, this field is marked by rapid innovation and profound impact.
Historical Overview
The journey began in the mid-20th century with large mainframe computers, which governments and corporations primarily used. The introduction of personal computers in the 1970s democratized access to technology, leading to widespread adoption.
Key Innovations
Microprocessors: These compact chips are the brains behind modern computers, enabling faster processing speeds and more efficient power usage.
Internet: The development of the internet has connected billions worldwide, facilitating communication and information exchange.
Mobile Computing: Smartphones and tablets have made computing portable, allowing users to access information anytime and anywhere.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to process information in fundamentally different ways than classical computers. Instead of bits (0s and 1s), quantum computers use qubits, which can represent and store more complex data due to their ability to simultaneously exist in multiple states. This allows them to solve certain problems much faster, such as factoring large numbers or simulating molecular structures.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, particularly computer systems. Machine learning, a subset of AI, involves algorithms that enable computers to learn from and make predictions based on data. Innovations include deep learning, natural language processing, and computer vision, leading to advancements in areas like autonomous vehicles, personalized medicine, and virtual assistants.
Edge Computing
Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed rather than relying on a central data center. This reduces latency and bandwidth use while improving response times for applications such as IoT devices, smart cities, and real-time analytics. It enhances performance for time-sensitive applications by processing data locally.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing resources over the Internet without direct user management. It enables scalable resources such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics. Key models include Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). This innovation has transformed how businesses operate by enhancing flexibility and reducing costs.
Cybersecurity Advances
As digital threats evolve, cybersecurity innovations focus on protecting systems from attacks through advanced encryption methods, intrusion detection systems (IDS), machine learning for threat detection, zero-trust architectures, and more robust authentication protocols like biometrics or multi-factor authentication (MFA). These advances aim to safeguard sensitive data against breaches and cyberattacks.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR overlays digital information onto the real world through devices like smartphones or AR glasses (e.g., Pokémon GO), while VR immerses users in entirely virtual environments using headsets (e.g., Oculus Rift). Both technologies are transforming sectors such as gaming, education (virtual classrooms), training simulations for various industries, architecture visualization tools, and remote collaboration.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is a decentralized ledger technology that securely records transactions across many computers so that the recorded transactions cannot be altered retroactively without altering all subsequent blocks—ensuring transparency and security. Beyond cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin Ethereum uses blockchain for smart contracts enabling automated agreements without intermediaries.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP enables computers to understand human language in text or speech form through linguistic analysis techniques combined with machine learning algorithms. Applications include chatbots for customer service automation, sentiment analysis tools for social media monitoring translation services like Google Translate, and voice-activated assistants like Siri or Alexa to enhance user interaction with technology.
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI)
HCI focuses on creating user-friendly interfaces between humans and computers through design principles aimed at improving usability, accessibility, efficiency, and satisfaction during interaction processes involving hardware, software applications, and input/output devices, making technology more intuitive and especially vital for diverse populations, including those with disabilities.
5G Technology
5G is the fifth generation of mobile network technology designed to significantly enhance speed capacity responsiveness compared to previous generations offering lower latency improved connectivity among devices supporting emerging technologies such as IoT smart cities autonomous vehicles providing seamless communication essential for real-time applications.
These innovations are shaping not only technological landscapes but also societal structures by driving efficiencies enhancing productivity creating new opportunities across various industrie
Emerging Technologies

Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is at the forefront of technological advancement, powering applications from virtual assistants to autonomous vehicles.
Blockchain: This decentralised ledger technology promises enhanced security and transparency across various sectors, including finance and supply chain management.
Quantum Computing: Although still in its infancy, quantum computing holds the potential to solve complex problems beyond the reach of classical computers
Impact on Society
Computer technology influences nearly every aspect of daily life:
Education: E-learning platforms have transformed traditional education models, making learning accessible globally.
Healthcare: Telemedicine and health informatics improve patient care through better data management and remote consultations.
Business: Automation and data analytics enhance efficiency and decision-making processes in organisations.
Future Trends
Looking ahead, several trends are shaping the future of computer technology:
Sustainability: As concerns about climate change grow, there is a push for greener technologies that reduce energy consumption.
Cybersecurity: With increasing digital threats, robust cybersecurity measures are essential to protect sensitive information.
Human-computer Interaction (HCI): Advancements in HCI will lead to more intuitive interfaces using voice recognition, gesture control, and augmented reality.
Conclusion
The realm of computer technology is dynamic and ever-evolving. As we embrace new innovations, it is crucial to consider their implications on society while striving for inclusivity and sustainability. The future promises exciting possibilities as we continue to explore this fascinating field.